2.3 工作机制 #
2.3.1 基本架构 #
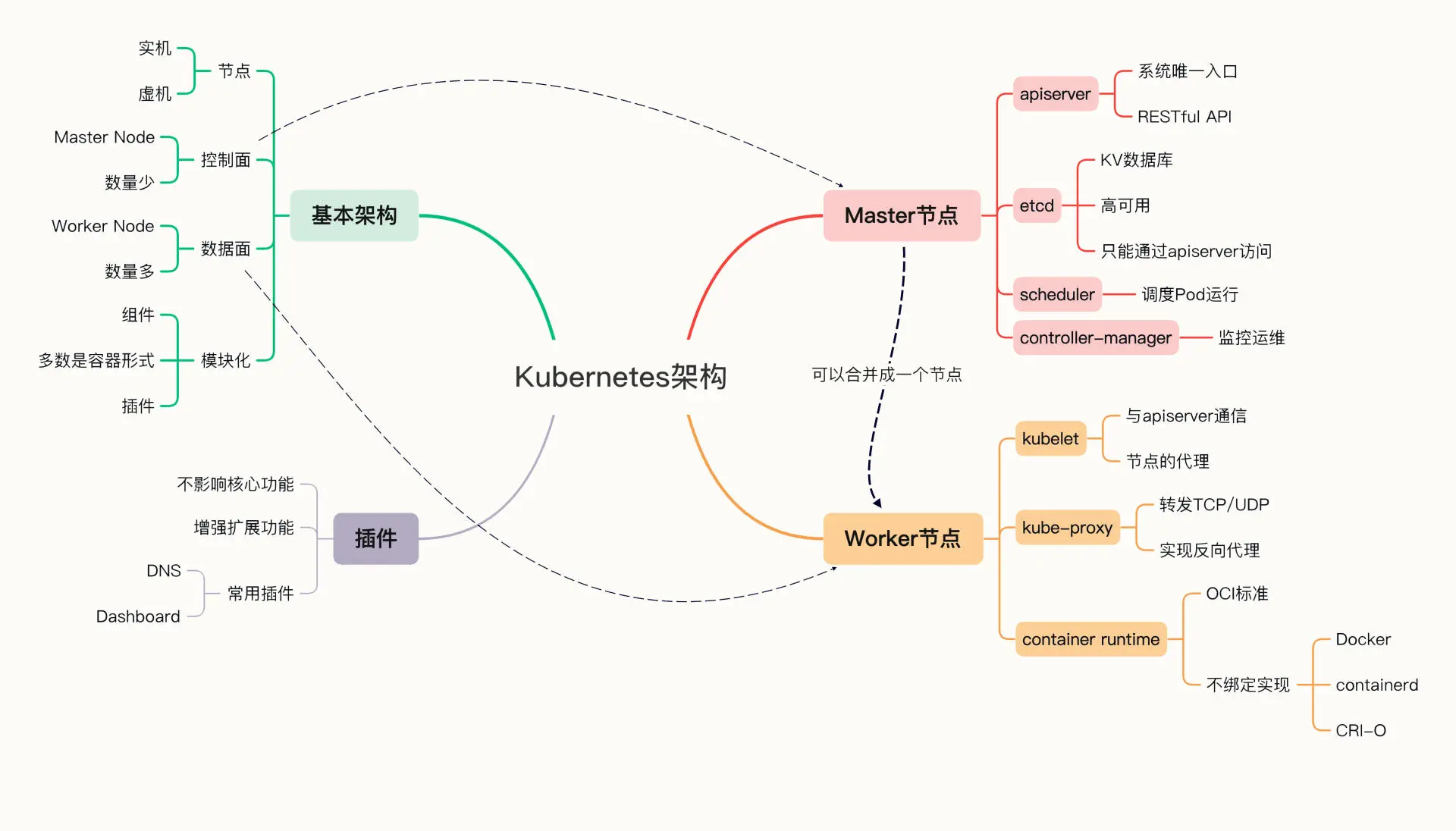
Kubernetes 采用了 “控制面 / 数据面”(Control Plane / Data Plane)架构,集群里的计算机被称为 “节点”(Node),可以是物理机也可以是虚拟机,少量的节点用作控制面来执行集群的管理维护工作,其他的大部分节点都被划归数据面,用来跑业务应用。
控制面的节点在 Kubernetes 里叫做 Master Node,一般简称为 Master,它是整个集群里最重要的部分,可以说是 Kubernetes 的大脑和心脏。数据面的节点叫做 Worker Node,一般就简称为 Worker 或者 Node,相当于 Kubernetes 的手和脚,在 Master 的指挥下干活。Node 的数量非常多,构成了一个资源池,Kubernetes 就在这个池里分配资源,调度应用。因为资源被 “池化”了,所以管理也就变得比较简单,可以在集群中任意添加或者删除节点。
Master 和 Node 的划分不是绝对的。当集群的规模较小,工作负载较少的时候,Master 也可以承担 Node 的工作,就像 minikube 环境,它就只有一个节点,这个节点既是 Master 又是 Node。
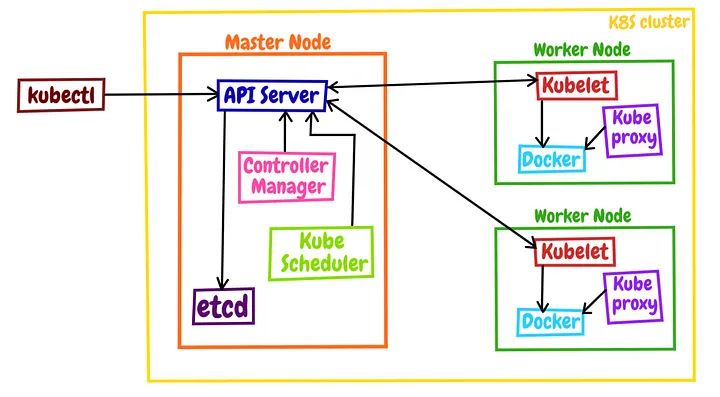
在下面这张架构图中,可以看到有一个 kubectl,它是 Kubernetes 的客户端工具,用来操作 Kubernetes,但它位于集群之外,理论上不属于集群。
2.3.2 节点内部结构 #
Kubernetes 的节点内部具有非常复杂的结构,由很多的模块构成的,这些模块又可以分成组件(Component)和插件(Addon)两类。
组件实现了 Kubernetes 的核心功能特性,没有这些组件 Kubernetes 就无法启动,而插件则是 Kubernetes 的一些附加功能,属于 “锦上添花”,不安装也不会影响 Kubernetes 的正常运行。
组件 #
Master 有 4 个组件,分别是 apiserver、etcd、scheduler、controller-manager。
apiserver 是 Master 节点,同时也是整个 Kubernetes 系统的唯一入口,它对外公开了一系列的 RESTful API,并且加上了验证、授权等功能,所有其他组件都只能和它直接通信,可以说是 Kubernetes 里的联络员。
etcd 是一个高可用的分布式 Key-Value 数据库,用来持久化存储系统里的各种资源对象和状态,相当于 Kubernetes 里的配置管理员。它只与 apiserver 有直接联系,也就是说任何其他组件想要读写 etcd 里的数据都必须经过 apiserver。
scheduler 负责容器的编排工作,检查节点的资源状态,把 Pod 调度到最适合的节点上运行,相当于部署人员。因为节点状态和 Pod 信息都存储在 etcd 里,所以 scheduler 必须通过 apiserver 才能获得。
controller-manager 负责维护容器和节点等资源的状态,实现故障检测、服务迁移、应用伸缩等功能,相当于监控运维人员。同样地,它也必须通过 apiserver 获得存储在 etcd 里的信息,才能够实现对资源的各种操作。
这 4 个组件也都被容器化运行在集群的 Pod 里,可以用 kubectl 来查看它们的状态:
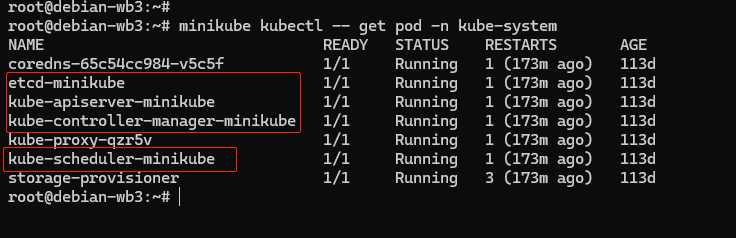
-n kube-system 参数,表示检查 “kube-system” 名字空间里的 Pod。
Node 里有 3 个组件,分别是 kubelet、kube-proxy、container-runtime。
kubelet 是 Node 的代理,负责管理 Node 相关的绝大部分操作,Node 上只有它能够与 apiserver 通信,实现状态报告、命令下发、启停容器等功能。
kube-proxy 的作用有点特别,它是 Node 的网络代理,只负责管理容器的网络通信,简单来说就是为 Pod 转发 TCP/UDP 数据包。
container-runtime 是容器和镜像的实际使用者,在 kubelet 的指挥下创建容器,管理 Pod 的生命周期。
Kubernetes 的定位是容器编排平台,所以它没有限定 container-runtime 必须是 Docker,完全可以替换成任何符合标准的其他容器运行时,例如 containerd、CRI-O 等。
工作流程 #
-
每个 Node 上的 kubelet 会定期向 apiserver 上报节点状态,apiserver 再存到 etcd 里。
-
每个 Node 上的 kube-proxy 实现了 TCP/UDP 反向代理,让容器对外提供稳定的服务。
-
scheduler 通过 apiserver 得到当前的节点状态,调度 Pod,然后 apiserver 下发命令给某个 Node 的 kubelet,kubelet 调用 container-runtime 启动容器。
-
controller-manager 也通过 apiserver 得到实时的节点状态,监控可能的异常情况,再使用相应的手段去调节恢复。

2.3.3 API 对象 #
作为一个集群操作系统,Kubernetes 归纳总结了 Google 多年的经验,在理论层面抽象出了很多个概念,用来描述系统的管理运维工作,这些概念就叫做 “API 对象”。
因为 apiserver 是 Kubernetes 系统的唯一入口,外部用户和内部组件都必须和它通信,而它采用了 HTTP 协议的 URL 资源理念,API 风格也用 RESTful 的 GET/POST/DELETE 等等,所以,这些概念很自然地就被称为是 “API 对象”。
可以使用 kubectl api-resources 来查看当前 Kubernetes 版本支持的所有对象:
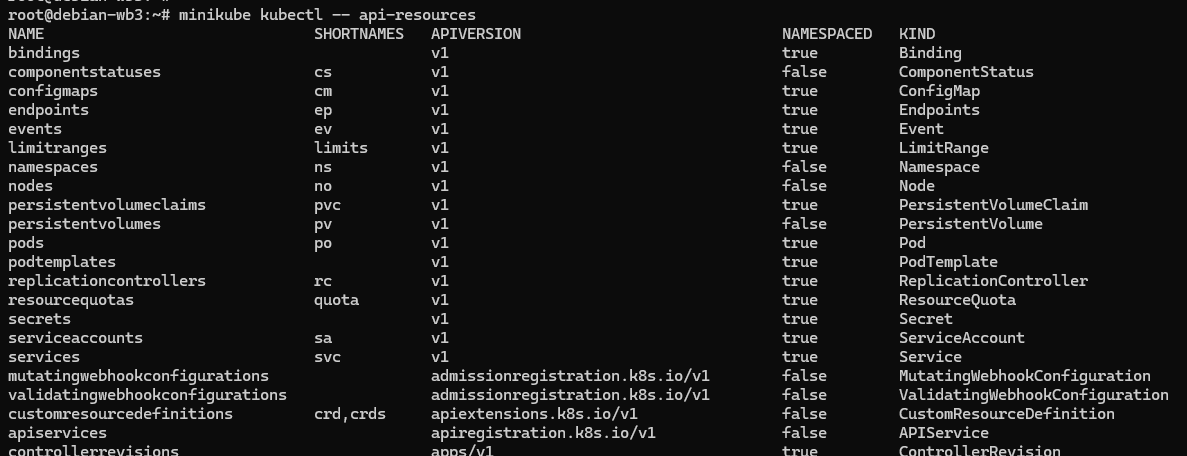
“NAME” 一栏,就是对象的名字,比如 ConfigMap、Pod、Service 等等,第二栏 “SHORTNAMES” 则是这种资源的简写。
在使用 kubectl 命令的时候,你还可以加上一个参数 –v=9,可以显示出详细的命令执行过程,清楚地看到发出的 HTTP 请求,比如:

root@debian-wb3:~# minikube kubectl -- get pod --v=9
I0511 16:16:12.470389 52352 loader.go:372] Config loaded from file: /root/.kube/config
I0511 16:16:12.471093 52352 cert_rotation.go:137] Starting client certificate rotation controller
I0511 16:16:12.474656 52352 round_trippers.go:466] curl -v -XGET -H "Accept: application/json;as=Table;v=v1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json;as=Table;v=v1beta1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json" -H "User-Agent: kubectl/v1.23.3 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/816c97a" 'https://192.168.49.2:8443/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods?limit=500'
I0511 16:16:12.475040 52352 round_trippers.go:510] HTTP Trace: Dial to tcp:192.168.49.2:8443 succeed
I0511 16:16:12.481955 52352 round_trippers.go:570] HTTP Statistics: DNSLookup 0 ms Dial 0 ms TLSHandshake 4 ms ServerProcessing 2 ms Duration 7 ms
I0511 16:16:12.482003 52352 round_trippers.go:577] Response Headers:
I0511 16:16:12.482030 52352 round_trippers.go:580] Cache-Control: no-cache, private
I0511 16:16:12.482074 52352 round_trippers.go:580] Content-Type: application/json
I0511 16:16:12.482102 52352 round_trippers.go:580] X-Kubernetes-Pf-Flowschema-Uid: 0bc68592-ae0d-443e-bdc8-020149821437
I0511 16:16:12.482155 52352 round_trippers.go:580] X-Kubernetes-Pf-Prioritylevel-Uid: baa7014e-a109-46a4-bf9b-1d2bc2998aac
I0511 16:16:12.482199 52352 round_trippers.go:580] Date: Thu, 11 May 2023 08:16:12 GMT
I0511 16:16:12.482236 52352 round_trippers.go:580] Audit-Id: 07a6c7e2-86fb-4d6b-b30c-ae132e098e9d
I0511 16:16:12.482346 52352 request.go:1181] Response Body: {"kind":"Table","apiVersion":"meta.k8s.io/v1","metadata":{"resourceVersion":"760475"},"columnDefinitions":[{"name":"Name","type":"string","format":"name","description":"Name must be unique within a namespace. Is required when creating resources, although some resources may allow a client to request the generation of an appropriate name automatically. Name is primarily intended for creation idempotence and configuration definition. Cannot be updated. More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/identifiers#names","priority":0},{"name":"Ready","type":"string","format":"","description":"The aggregate readiness state of this pod for accepting traffic.","priority":0},{"name":"Status","type":"string","format":"","description":"The aggregate status of the containers in this pod.","priority":0},{"name":"Restarts","type":"string","format":"","description":"The number of times the containers in this pod have been restarted and when the last container in this pod has restarted.","priority":0},{"name":"Age","type":"string","format":"","description":"CreationTimestamp is a timestamp representing the server time when this object was created. It is not guaranteed to be set in happens-before order across separate operations. Clients may not set this value. It is represented in RFC3339 form and is in UTC.\n\nPopulated by the system. Read-only. Null for lists. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata","priority":0},{"name":"IP","type":"string","format":"","description":"IP address allocated to the pod. Routable at least within the cluster. Empty if not yet allocated.","priority":1},{"name":"Node","type":"string","format":"","description":"NodeName is a request to schedule this pod onto a specific node. If it is non-empty, the scheduler simply schedules this pod onto that node, assuming that it fits resource requirements.","priority":1},{"name":"Nominated Node","type":"string","format":"","description":"nominatedNodeName is set only when this pod preempts other pods on the node, but it cannot be scheduled right away as preemption victims receive their graceful termination periods. This field does not guarantee that the pod will be scheduled on this node. Scheduler may decide to place the pod elsewhere if other nodes become available sooner. Scheduler may also decide to give the resources on this node to a higher priority pod that is created after preemption. As a result, this field may be different than PodSpec.nodeName when the pod is scheduled.","priority":1},{"name":"Readiness Gates","type":"string","format":"","description":"If specified, all readiness gates will be evaluated for pod readiness. A pod is ready when all its containers are ready AND all conditions specified in the readiness gates have status equal to \"True\" More info: https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-network/580-pod-readiness-gates","priority":1}],"rows":[{"cells":["ngx","1/1","Running","1 (4h30m ago)","113d","172.17.0.2","minikube","\u003cnone\u003e","\u003cnone\u003e"],"object":{"kind":"PartialObjectMetadata","apiVersion":"meta.k8s.io/v1","metadata":{"name":"ngx","namespace":"default","uid":"9141b021-f735-4d4f-97d7-a16ba477312b","resourceVersion":"749131","creationTimestamp":"2023-01-17T14:20:09Z","labels":{"run":"ngx"},"managedFields":[{"manager":"kubectl-run","operation":"Update","apiVersion":"v1","time":"2023-01-17T14:20:09Z","fieldsType":"FieldsV1","fieldsV1":{"f:metadata":{"f:labels":{".":{},"f:run":{}}},"f:spec":{"f:containers":{"k:{\"name\":\"ngx\"}":{".":{},"f:image":{},"f:imagePullPolicy":{},"f:name":{},"f:resources":{},"f:terminationMessagePath":{},"f:terminationMessagePolicy":{}}},"f:dnsPolicy":{},"f:enableServiceLinks":{},"f:restartPolicy":{},"f:schedulerName":{},"f:securityContext":{},"f:terminationGracePeriodSeconds":{}}}},{"manager":"Go-http-client","operation":"Update","apiVersion":"v1","time":"2023-05-11T03:46:17Z","fieldsType":"FieldsV1","fieldsV1":{"f:status":{"f:conditions":{"k:{\"type\":\"ContainersReady\"}":{".":{},"f:lastProbeTime":{},"f:lastTransitionTime":{},"f:status":{},"f:type":{}},"k:{\"type\":\"Initialized\"}":{".":{},"f:lastProbeTime":{},"f:lastTransitionTime":{},"f:status":{},"f:type":{}},"k:{\"type\":\"Ready\"}":{".":{},"f:lastProbeTime":{},"f:lastTransitionTime":{},"f:status":{},"f:type":{}}},"f:containerStatuses":{},"f:hostIP":{},"f:phase":{},"f:podIP":{},"f:podIPs":{".":{},"k:{\"ip\":\"172.17.0.2\"}":{".":{},"f:ip":{}}},"f:startTime":{}}},"subresource":"status"}]}}}]}
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ngx 1/1 Running 1 (4h30m ago) 113d
可以看到,kubectl 客户端等价于调用了 curl,向 8443 端口发送了 HTTP GET 请求,URL 是 /api/v1/namespaces/default/pods。
如何描述 #
可以使用 YAML 描述并创建 API 对象。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: ngx-pod
labels:
env: demo
owner: xiaobinqt
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:alpine
name: ngx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
-
apiVersion 表示操作这种资源的 API 版本号,由于 Kubernetes 的迭代速度很快,不同的版本创建的对象会有差异,为了区分这些版本就需要使用 apiVersion 这个字段,比如 v1、v1alpha1、v1beta1 等等。
-
kind 表示资源对象的类型,这个应该很好理解,比如 Pod、Node、Job、Service 等等。
-
metadata 表示的是资源的一些 “元信息”,也就是用来标记对象,方便 Kubernetes 管理的一些信息。一般来说,“metadata” 里应该有 name 和 labels 这两个字段。
apiVersion、kind、metadata 这三个字段是任何对象都必须有的,由于每种对象会有不同的规格定义,在 YAML 里就表现为 spec 字段(即 specification),表示我们对对象的 “期望状态”(desired status)。
以下的这个 spec 里是一个 containers 数组,里面的每个元素又是一个对象,指定了名字、镜像、端口等信息:
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:alpine
name: ngx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
如何使用 #
使用 kubectl apply、kubectl delete,加上参数 -f 指定描述的 YAML 文件,就可以创建或者删除对象了:
kubectl apply -f ngx-pod.yml
kubectl delete -f ngx-pod.yml
Kubernetes 收到 YAML 声明的数据,再根据 HTTP 请求里的 POST/DELETE 等方法,就会自动操作这个资源对象,至于对象在哪个节点上、怎么创建、怎么删除完全不用使用者操心。
编写 YAML 描述 #
kubectl explain,相当于是 Kubernetes 自带的 API 文档,会给出对象字段的详细说明。比如想要看 Pod 里的字段该怎么写,就可以这样:
kubectl explain pod
kubectl explain pod.metadata
kubectl explain pod.spec
kubectl explain pod.spec.containers
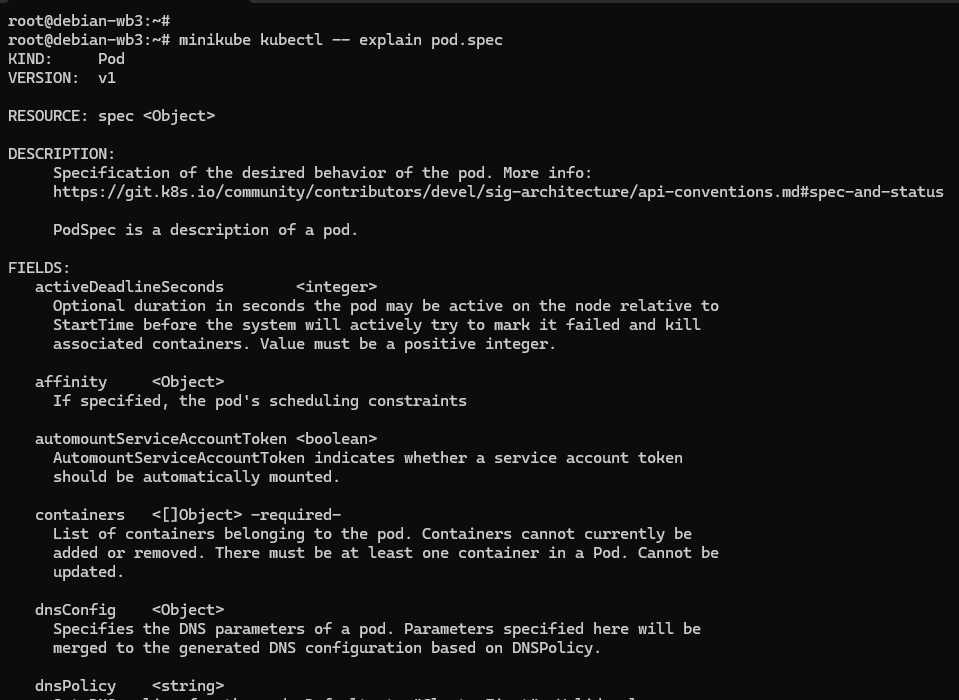
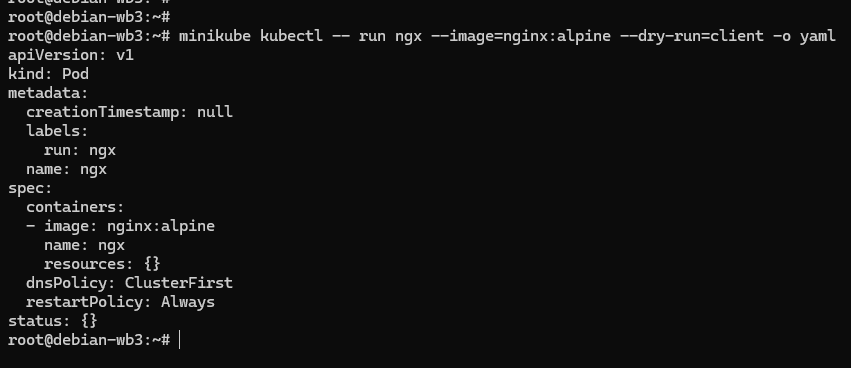
kubectl 的两个特殊参数 --dry-run=client 和 -o yaml,前者是空运行,后者是生成 YAML 格式,结合起来使用就会让 kubectl 不会有实际的创建动作,而只生成 YAML 文件。
例如,想要生成一个 Pod 的 YAML 样板示例,可以在 kubectl run 后面加上这两个参数:
kubectl run ngx --image=nginx:alpine --dry-run=client -o yaml